An angle of elevation is an angle with one horizontal arm, and one arm above horizontal.
Usually an angle of elevation is less than or equal to 90°.
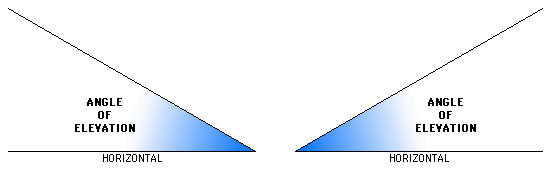
An angle of elevation is an angle with one horizontal arm, and one arm above horizontal.
Usually an angle of elevation is less than or equal to 90°.

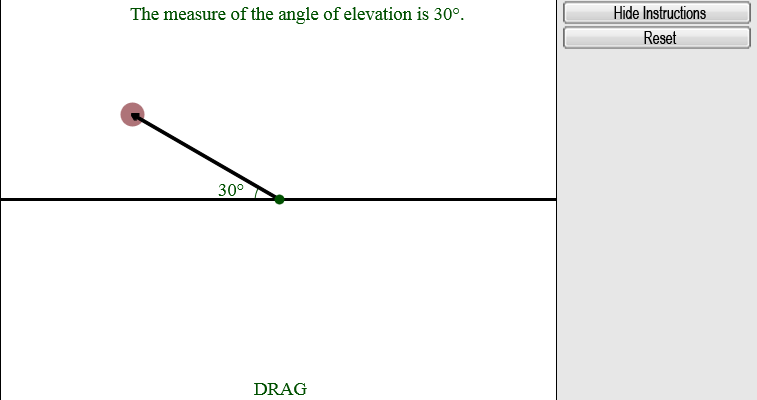 Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js
Image onlyInstructions text as in global.jsAn angle of elevation of one location relative to another is always congruent (equal in measure) to the angle of depression of the first location relative to the second.
In the illustration below, the angle of elevation of the bird relative to the cat is equal in measure to the angle of depression of the cat relative to the bird.

The "line of sight" forms a transversal of the two horizontal parallel lines. As a result the angles of elevation and depression are alternate (interior) angles.
Since the transversal intersects two parallel lines, and alternate interior angles are congruent, the angle of elevation and angle of depression must also be congruent.
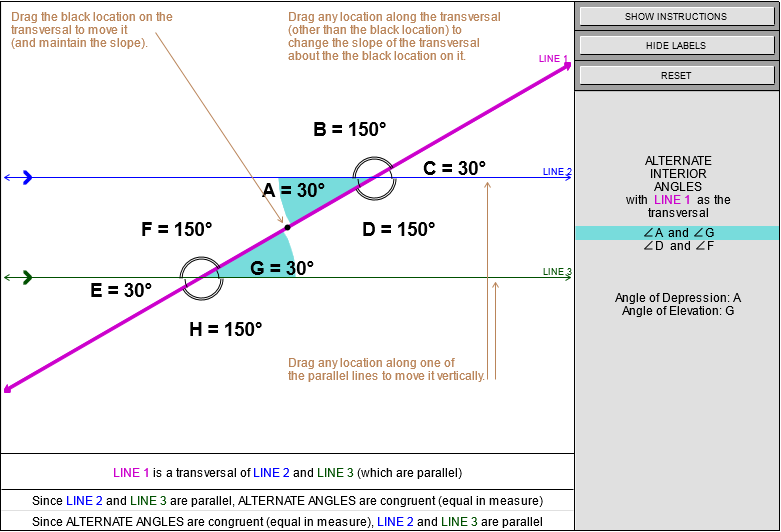 Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js
Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js